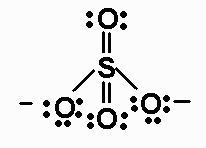
1.a) Draw resonance forms for
SO32- 26 valence electrons

CO32- 24 valence electrons
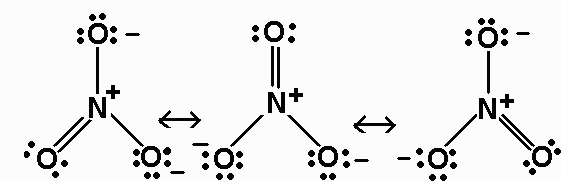
NO3- 24 valence electrons
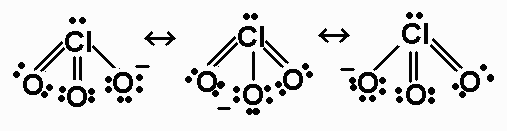
ClO3- 26 valence electrons
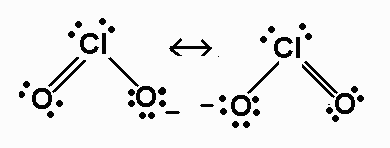
ClO2- 20 valence electrons
b) What are the bond orders for the central-atom-to-oxygen bonds
in these species?
For SO32-, the bond order is 4/3.
For CO32-, the bond order is 4/3.
For NO3-, the bond order is 4/3.
For ClO3-, the bond order is 5/3.
For ClO2-, the bond order is 3/2.br>
c) What is the average formal charge on the oxygen atoms in each
of these species?
The average formal charge on oxygen in SO32-
is -2/3.
The average formal charge on oxygen in CO32-
is -2/3.
The average formal charge on oxygen in NO3-
is -2/3 (note that N has a formal charge of +1 in this ion).
The average formal charge on oxygen in ClO3-
is -1/3.
The average formal charge on oxygen in ClO2-,
is -1/2.
d) Choose all of the species of part a that violate the octet
rule.
The species that violate the octet rule are SO32-,ClO3-, and ClO2-
e) Give the AXnEm classes and predict the
shapes of all the
anions.
SO32- - AX3E - triangular
pyramidal
CO32- - AX3 - triangular
planar
NO3- - AX3 - triangular planar
ClO3- - AX3E - triangular
pyramidal
ClO2- - AX2E2 -
bent
2. Oxalic acid, (COOH)2, has two ionizable hydrogens
and contains
a carbon-carbon single bond. When one mole of oxalic acid reacts
with one mole of
calcium hydroxide,Ca(OH)2, the salt
CaC2O4 is
formed.
a) Draw adequate Lewis structures to represent the bonding in
the oxalate ion,
C2O42-.
There are 34 valence electrons.

b) What is the carbon-oxygen bond order in oxalate ion?
Bond order = (1 + 2 + 1 + 2)/4 = 1.5
c) What is the formal charge on each oxygen atom in oxalate
ion?
Formal charge on oxygen = (-1 + 0 + (-1) + 0)/4 = -1/2
3. N2O has a linear, unsymmetrical structure that may
be thought
of as a hybrid of two resonance forms. Draw the two resonance
forms of
N2O.
There are 16 valence electrons. (Also remember that N and O obey
the octet rule.)
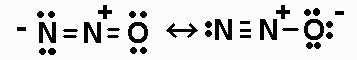
4. A solid non-metallic element (A) from Group 5A was burned in
excess oxygen to give a
white solid (B) (Rxn 1). The white solid (B) dissolves in water to
give a solution of a substance
(C) (Rxn 2); (C) turns blue litmus red. To this solution of (C)
was added an excess of aqueous
KOH to produce an aqueous solution of (D) (Rxn 3). Write balanced
equations for Rxns 1, 2,
and 3; identify A, B, C, D.
Reaction 1: P4(s) + 5O2(g) -->
P4O10(s).
Thus A is P4, and B is P4O10
Reaction 2:P4O10(s) + 6H2O(l) -->
4H3PO4(aq). Thus C is
H3PO4.
Reaction 3:H3PO4(aq) + 3KOH(aq) -->
K3PO4(aq) + 3H2O(l). Thus D is
K3PO4.
5. Phosphoric acid, H3PO4, contains three
oxygen-hydrogen single
bonds. When one mole of phosphoric acid reacts with one mole of
sodium hydroxide,
the salt sodium dihydrogen phosphate,
NaH2PO4, results.
a) Draw adequate Lewis structures for H3PO4
and
H2PO4-.
H3PO4 has 32 valence electrons.

H2PO4- has 32 valence
electrons.
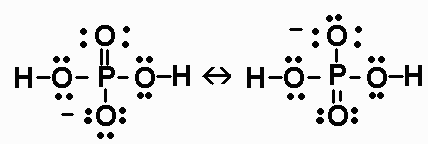
b) Calculate bond orders for all the phosphorus-oxygen bonds of
H3PO4 and
H2PO4-.
In H3PO4, there is one P-O bond of bond order
2, and three P-O bonds
of bond order 1.
In H2PO4-, there are two P-O bonds
of bond order 1.5,
and two P-O bonds of bond order 1.
c) Calculate the formal charges on each oxygen atom in
H3PO4
and
H2PO4-.
In H3PO4, all oxygen atoms have a formal
charge of zero.
In H2PO4-, two oxygen atoms
(bonded to H) have a
formal charge of zero, while the other tow have a formal charge of
-1/2.
6. For the molecules OCS, ICl3, IF5,
SO2,
PF3, and CCl2Br2:
a) determine the AXnEm class;
b) decide which have dipole moments, and for those that do, decide
the direction of
the dipole moment.
OCS has 16 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure (with bond
moments shown) is
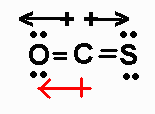
It is an AX2 molecule, with a net dipole moment pointing
to O.
ICl3 has 28 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
(with bond moments shown)
is
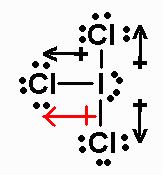
It is an AX3E2 molecule, with a net dipole
moment pointing towards
the equatorial Cl (the two axial bond moments cancel).
IF5 has 42 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
is
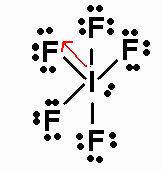
It is an AX5E molecule, with a net dipole moment
pointing to the fluorine that is
situated 180o from the nonbonding pair.
SO2 has 18 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
is
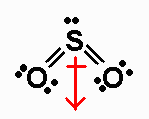
It is an AX2E molecule, with a net dipole moment
pointing from S to a point
midway between the O atoms.
PF3 has 26 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
is
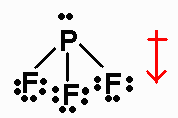
It is an AX3E molecule, with a net dipole moment
pointing from P to the center of
the triangle formed by the three fluorines.
CCl2Br2 has 32 valence electrons. Its Lewis
structure is
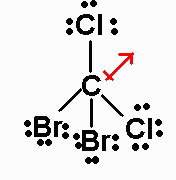
It is an AX4 molecule, with a net dipole moment pointing
from C and bisecting the
Cl-C-Cl angle.
7. A gaseous molecule "X" is made by burning a yellow elemental
solid in air. "X" is
converted to "Y" by reaction with oxygen in the presence of a
catalyst. "Y" reacts
vigorously with water to produce "Z" which turns litmus red.
a) Identify "X", "Y", and "Z".
"X" = SO2, "Y" is SO3, and "Z" is
H2SO4.
b) Write a balanced equation for each reaction.
S(s) + O2(g) --> SO2(g)
2SO2(g) + O2(g) --> 2SO3(g)
SO3(g) + H2O(l) -->
H2SO4(aq)
c) Draw Lewis diagrams and indicate the shapes of the molecules
"X" and "Y".
SO2 has 18 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
is

The molecule is AX2E, and is bent.
SO3 has 24 valence electrons. Its Lewis structure
is

The molecule is AX3, and is triangluar planar.
d) State whether "X" and "Y" possess dipole moments and, if so,
in which direction
they point.
SO2 has a dipole moment pointing from S to midway
between the oxygen
atoms.
SO3 has no dipole moment.
e) When 1 mole of "Z" is titrated with 2 moles of NaOH, a
soluble salt "W" forms. Write
an appropriate Lewis electron dot structure for the anion of this
salt.
"W" is SO42-. There are six resonance
structures. One of them is