
| Problem Set #10 | ANSWERS | January 10, 1997 |
1. Give the structures corresponding to each of the following IUPAC names
a) 3-ethoxy-2-methylhexane
b) 4-methyl-2-pentanol
c) 4-t-butyl-3-methoxyheptane
d) 1,6-hexanediol
Answers

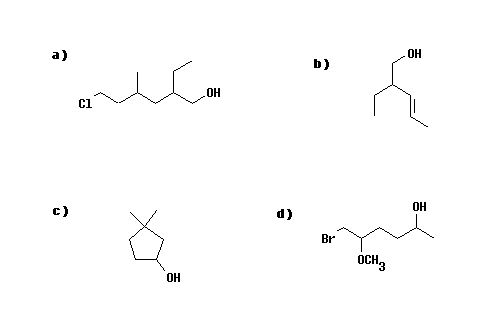
Answers
a) 6-chloro-2-ethyl-4-methylhexan-1-ol (Note alphabetical order of substituents)
b) 2-ethylpent-3-en-1-ol (Note the alcohol group takes precedence)
c) 3,3-dimethylcyclopentan-1-ol
d) 6-bromo-5-methoxyhexan-2-ol
a) CH3CH 2CH 2OH treated with concentrated H2SO4 at 130 oC.
b) CH3CH 2CH2O- + (CH3) 3CCl
c) (CH3) 3CO- + CH3CH 2CH 2Cl
d) (CH3) 3CCH 2OH Heated with HBr
e)
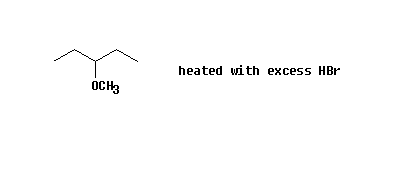
f)

Answers
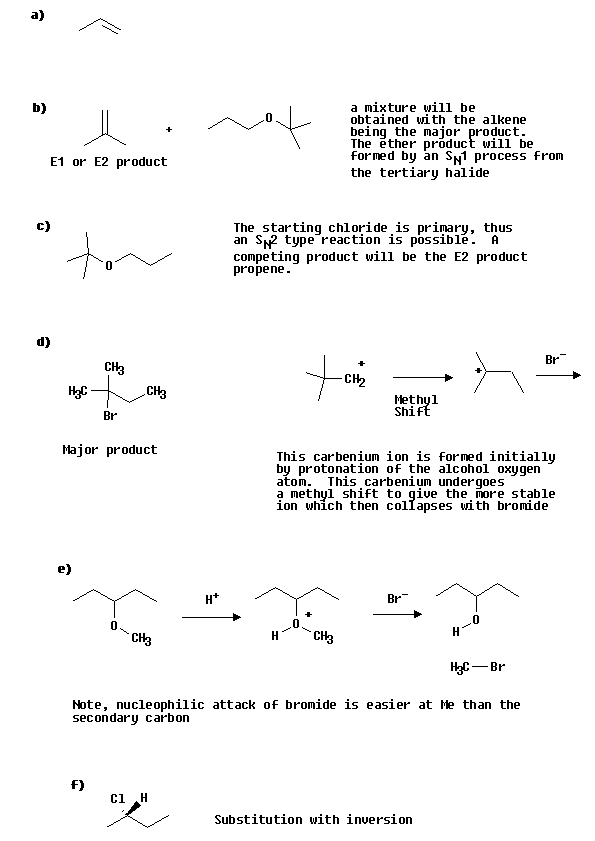
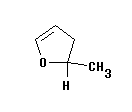
Answers
The approach to this problem is simple. The result can be quite complex as you will see below.
Step 1.
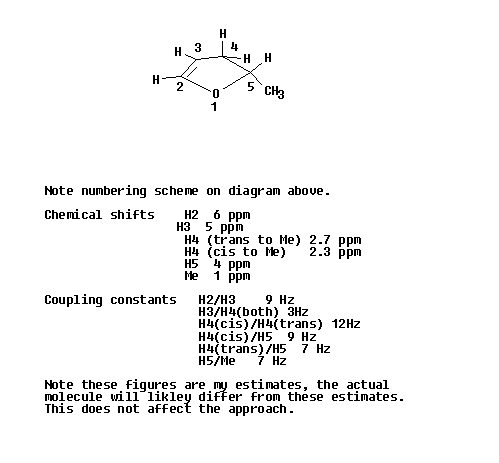
Identify all of the different hydrogens in the molecule. Here you need to be carefull with the molecule in question as the two hydrogens of the CH2 a different from each other, one being cis and the other trans to the methyl group. (Make a model to see this if needed.)
Step 2.
Use tables to identify the chemical shifts of each of the hydrogens in step one. Draw these out on a sheet of paper showing a single line for each resonance.
Step 3.
Back to tables and obtain your best guess at the coupling constant for each interaction. In terms of the answer to this problem we will only consider the large coupling contants over two and three bonds and not long range coupling constants which could be observed with a modern high field instrument.
Step 4.
Take each of the lines you drew out in step 2 in turn and sketch in the coupling tree. In each case it will be simplest to start with the largest coupling contant, draw this, and then apply the second coupling constant, etc. This is shown on the diagram below.

| Go to: |
Instructions for Printing this Document Chem2O6 Problem Sets & Answers Chem2O6 Home Page. |
10 jan 97; rfc