- 16.1 - .7 inclusive.
16.29
16.30 a), b) compounds B and C, c), and g).
16.31 a) and b)
16.36
16.37
16.42
16.43.
In addition you are welcome to try your hand at the following.......
1.This problem finds its basis in industrial organic chemistry. It concerns the manufacture and then uses of 2-ethylhexan-1-ol.
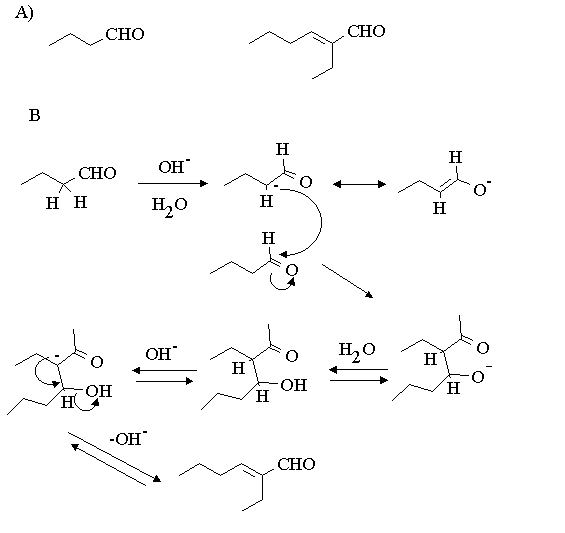
Butanal reacts in the presence of base in water as a solvent to form 2-ethyl-hex-2-enal
.
-
A) Write out the structures of butanal and 2-ethyl-hex-2-enal.
B) Write out a detailed mechanism for this reaction. (Note both steps are base catalysed.)
C) 2-Ethyl-hexanol can be produced from 2-ethyl-hex-2-enal. How would you carry out this transformation? (More than one reaction might be required.)
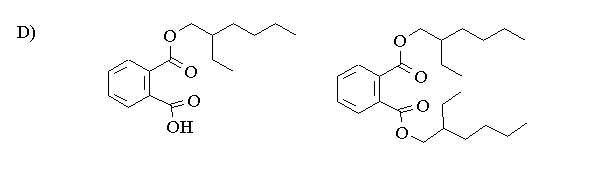
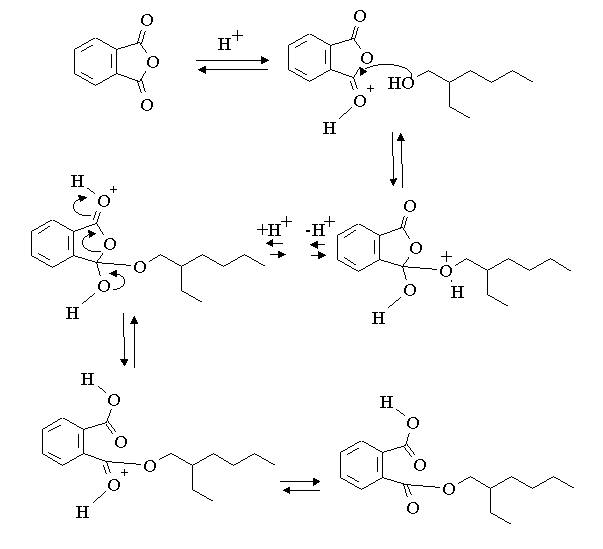
2-Ethyl-hexanol can be reacted with phthalic anhydride to form first a monoester and subsequently a diester. The reactions are acid catalysed and carried out with excess 2-ethyl-hexanol.
D) Give the structures of the mono and diesters.
E) Give a mechanism for the formation of the monoester.
You may be interested to know that the diester is widely used as a physiologically harmless plasticizer. That is it is added to common plastics to make them more flexible and soft to the touch. The ‘new car smell’, assuming you cannot afford leather seats, is most likley due to traces of compounds such as this diester. The diester can also be used as a replacement fluid for polychlorinated biphenyls in electrical applications.

2.The molecule shown below can be treated with D2O/OD- to give the di-deuterated product. However, prolonged treatement never leads to exchange of the other adjacent hydrogen marked with an asterix. Why not???? Hint, make a molecular model and think carefully of the structures of the two possible enolates.
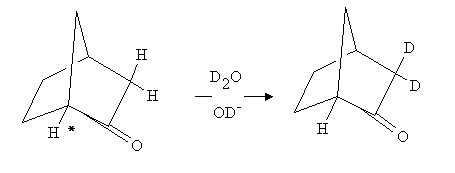
This question depends on you understanding the steric requirements for the formation of an enolate anion. For this to happen one must be able to conjugate the anion formed on the -carbon with the adjacent carbonyl. This means that the p-orbital on the -carbon must be able to line up with the p-orbital on the carbonyl carbon. This is impossible for the hydrogen marked * in the molecule. Make a model and convince yourself that this is the case.
| Go to: |
Instructions for Printing this Document Chem2O6 Problem Sets & Answers Chem2O6 Home Page. |
13 Feb 98; jp