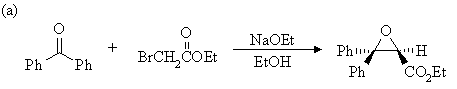
McMaster University - Chem3D03
| Problem Set #8 | ANSWERS | March 10, 1998 |
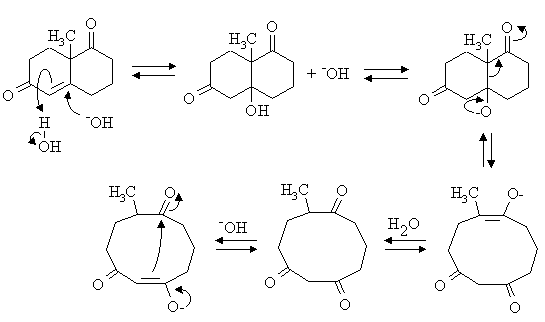
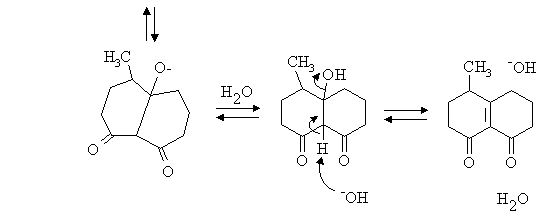
1. Write mechanisms for the following reactions:
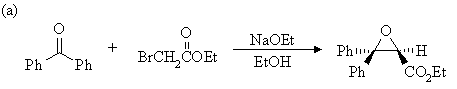
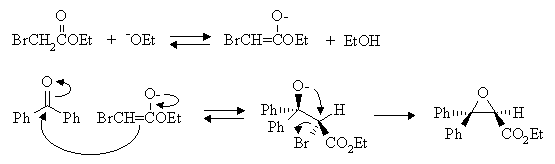
Answer:
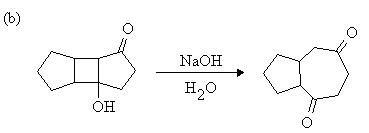
Answer:
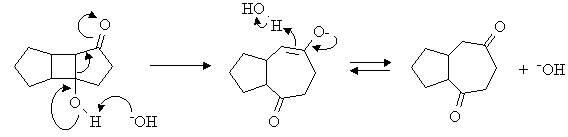
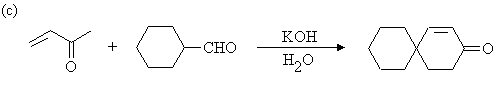
Answer:
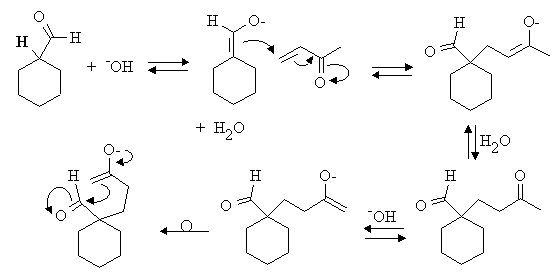
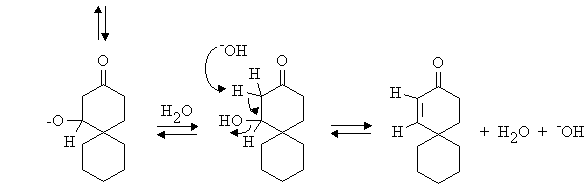
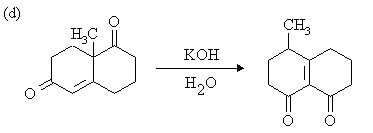
Answer:
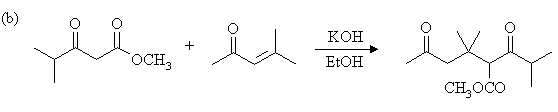
2. Draw the expected products of each of the reactions below, showing stereochemistry where appropriate.
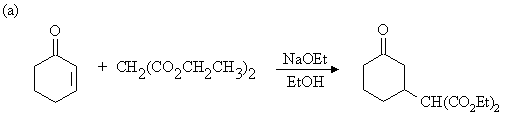
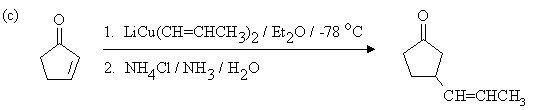
3. The structure of the product suggests that it arises from attack of the deprotonated aldehyde on the C=O of another:
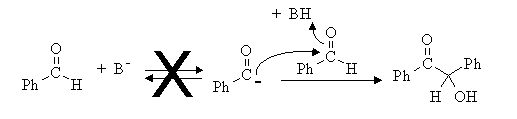
This cannot happen because the aldehydic proton is just NOT acidic; even a strong base like LDA will not deprotonate an aldehyde at this position. The reaction proceeds in the presence of cyanide ion because of the formation of the cyanohydrin. In the cyanohydrin, the old aldehydic proton is now acidic because the anion formed by its removal is stabilized by resonance with the cyano group. Now we have a nucleophile which can attack another aldehyde C=O to form the new C-C bond. Protonation, deprotonation, and loss of cyanide ion forms the product, benzoin, and regenerates the catalyst.

The self-condensation of aromatic aldehydes catalysed by cyanide ion is called the Benzoin Condensation
| Go to: | Instructions for Printing this Document Chem3D3 Problem Sets & Answers Chem3D3 Home Page. |
10mar98; wjl